Eczema
What is Eczema? Manage Your Eczema with Expert Care at Keystone Dermatology Partners
Eczema, or dermatitis, is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation, swelling, and irritation. It affects up to 35 million Americans, causing discomfort and, in some cases, complications like infections, although it is not considered dangerous.
At Keystone Dermatology Partners, our skin specialists are dedicated to providing personalized care tailored to your specific symptoms and triggers. For those with eczema, it is crucial to collaborate with a skincare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that meets your unique needs and effectively manages the condition.
With the right care and support, you can regain confidence in your skin and better manage your eczema. Discover more about eczema below, and let us help you find the best strategies to care for your skin and live more comfortably.
Examples of Eczema
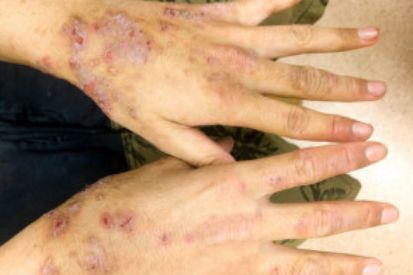

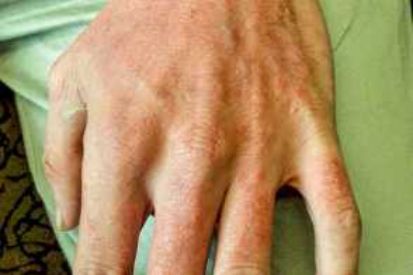
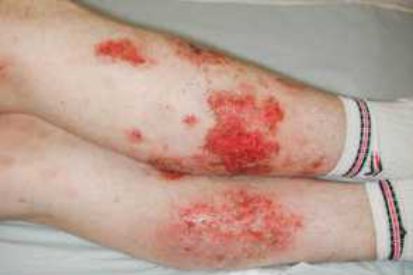
Eczema Symptoms
- Dry skin
- Itchy and flaky skin
- Irritated and inflamed skin
- Flare-ups can reoccur
- Affects the scalp and cheeks, inner elbows, behind the knees, and arms
- Often on the faces of young children
Managing Eczema Symptoms
- No cure for Eczema
- Medications
- Light therapy
- Quality sleep can help
- Make lifestyle changes that reduce your stress
- Avoid scratching
- Antihistamines
Types of Eczema
Contact Dermatitis: Skin irritation caused by an irritant. The inflammation subsides once the irritant is eliminated.
Dyshidrotic Dermatitis: This form of eczema occurs on the soles of the feet, fingers, and palms. It is marked by scaly skin patches that become itchy, cracked, painful, and red. This occurs more often in women.
Nummular Dermatitis: This condition occurs frequently in men. It shows up as round patches of dry skin, typically on the legs.
Eczema Frequently Asked Questions:
Eczema flare-ups can be triggered by allergens, irritants, environmental factors, stress, and even changes in temperature or humidity. Additionally, certain skincare products, soaps, and detergents, as well as emotional stress or anxiety, can contribute to the worsening of symptoms.
Eczema is a non-contagious skin condition and cannot be spread to others.
Yes, eczema can affect people at any stage of life, from infants to older adults. It often begins in childhood but can develop or persist into adulthood. Regardless of age, eczema can cause discomfort and require ongoing management to keep symptoms under control.
Although eczema cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments. By using prescribed medications, adopting a skincare routine tailored to sensitive skin, and avoiding known triggers, many people with eczema can significantly reduce flare-ups and maintain healthier skin.
Gentle skincare routines, like using mild, fragrance-free soaps, avoiding hot water, and consistently applying rich moisturizers, can significantly alleviate eczema symptoms. It’s also beneficial to choose products specifically designed for sensitive skin, limit exposure to harsh chemicals, and pat the skin dry gently after bathing. Regularly moisturizing immediately after bathing helps lock in moisture, keeping the skin hydrated and reducing the likelihood of flare-ups.
Dermatologists play a crucial role in managing eczema. They diagnose eczema accurately by assessing medical history and symptoms, and they create individualized treatment plans. These plans often include skincare routines, medications like corticosteroids or antihistamines, and advice on avoiding triggers and making lifestyle changes.
From our QualDerm Family of Brands: Eczema Symptoms
Treatment Options for Eczema
Oral Medications: Over-the-counter antihistamines are often recommended to relieve the itching. This class of medications blocks the body’s histamine response, which is responsible for causing allergic reactions. Examples of antihistamines include Loratadine, Cetirizine, and Fexofenadine. Over-the-counter medications can be easily obtained from any drug store. However, it is recommended that you consult with our dermatologists before taking these medications.
Topical Treatments: Steroid-based skin ointments and creams like cortisone can help provide relief from the scaling and itching. Low-potency steroids like hydrocortisone are readily available as over-the-counter solutions. If you are not responding well to these medications, your dermatologist may prescribe higher-potency steroids. Higher-potency antihistamines require a prescription.
Light Therapy: Also called phototherapy, this treatment uses sun lamps or ultraviolet lamps to stop your immune system from producing reactions that elicit eczema. Multiple light therapy sessions are required. This treatment can clear up and/or reduce your eczema. Light therapy treatments using sun lamps or ultraviolet lamps can be conducted in an office environment or at home.
Featured Blogs
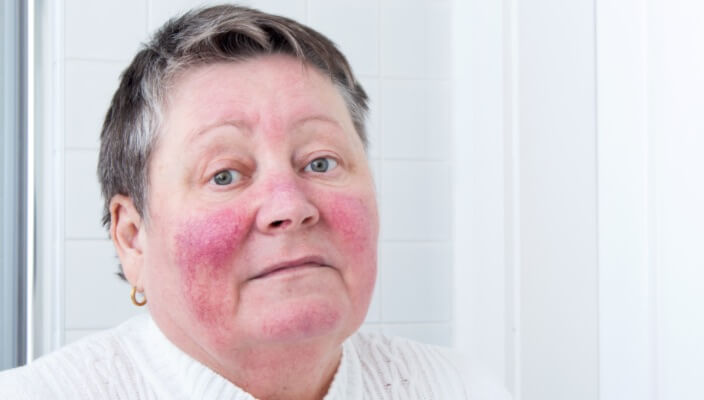

- General Dermatology
- Skin Care
Rosacea is a common skin condition characterized by facial redness and pimples. A recent study suggests that drinking caffeinated coffee may reduce the risk of developing rosacea, highlighting a potential benefit of coffee consumption.
Read More
- General Dermatology
- Chronic Skin Conditions
Discover how a dermatologist father identified and managed molluscum contagiosum, a common and benign skin infection, after noticing skin-colored bumps on his son.
Read More
- General Dermatology
Almost everyone experiences itchy skin at some point. Read this blog to learn how a dermatologist can help.
Read More

